Structure of Japan’s Digital Broadcasting Standard
1. Structure of technical standard for digital broadcasting
Generally speaking, Digital broadcasting system is composed by 3 functional blocks, (1) Source coding block, (2) Multiplex block, and (3) Transmission coding block.
The structure of Japan’s Digital broadcasting system is shown in Figure 1.
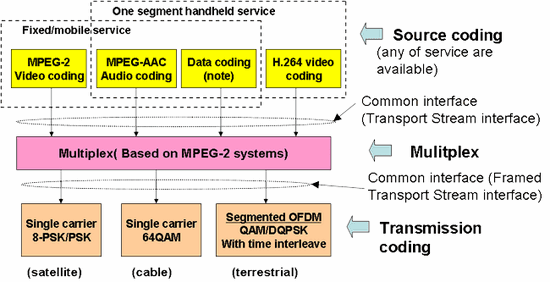
Figure 1: Structure of Japan’s Digital Broadcasting system
As shown in Figure, “Source coding” and “Multiplex” are common for any digital broadcasting media.
For “transmission coding”, the different coding technologies are adopted for each transmission media to optimize for transmission characteristics.
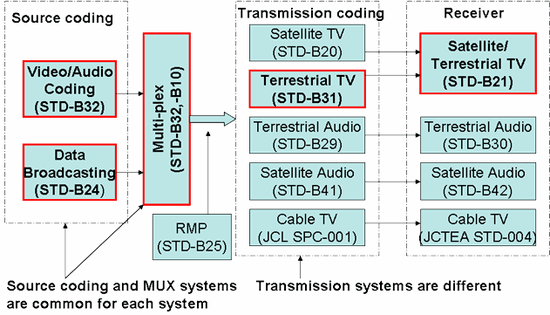
Figure 2: Structure of Technical Standards for Japan’s digital broadcasting
Figure 2 shows the structure of Technical Standards for Japan’s digital broadcasting. The standards for satellite / terrestrial broadcasting are standardized at ARIB (You will leave the DiBEG website). The standard of cable transmission system are standardized at another consortium. ARIB standards for digital broadcasting are described in Table 1.
| Digital Television | Digital Sound | Download(*1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satellite | Terrestrial | Terrestrial | Satellite | ||
| Transmission System | STD-B20 | STD-B31 | STD-B29 | STD-B41 | List of Standards for Broadcasting (ARIB website) (You will leave the DiBEG website) |
| Multiplex | Coding & Multiplexing STD-B32 | ||||
| Service Information STD-B10 | |||||
| Source coding | Coding & Multiplexing STD-B32 | ||||
| Data Broadcasting | Presentation Engine (BML) STD-B24 | ||||
| Execution Engine (GEM-based) STD-B23 | |||||
| CAS | Conditional Access STD-B25 | ||||
| Home servers | System based on Home Servers STD-B38 | ||||
| Receivers | STD-B21 | STD-B30 | STD-B42 | ||
| Operational Guidelines | TR-B15 | TR-B14(*2) | TR-B13 | TR-B26 | List of Technical Reports for Broadcasting (ARIB website) (You will leave the DiBEG website) |
*1 :These ARIB STD and TR are downloaded from ARIB website (You will leave the DiBEG website).
*2 :The content of TR-B14 Volume 9 Chapter 4 and Appendix A “Technological Explanation” has been updated and the latest version is included in ITU-R Report BT.2209-1 (You will leave the DiBEG website).
2. About ISDB-T transmission system
Japanese digital terrestrial broadcasting system adopts excellent technologies on transmission system.
The features of transmission system are as follows:
(1) Efficient frequency utilization
(b) Adopt hierarchical transmission to realize the different reception service in the same frequency band.
(b) Partial reception: handheld service in the same channel
(b) Time interleave: very effective against impulse noise
(5) Commonality of TV / audio transmission system
(6) Auxiliary (AC) channel can be used for transmission network management
3. Outline of transmission parameter
ISDB-T transmission system has the flexibility for adjusting various kinds of broadcasting service.
In Table 2, Outline of ISDB-T transmission parameters are shown.
For the details of transmission parameters, see ARIB STD-B31(∗).
∗ : ARIB STD is downloaded from List of Standards for Broadcasting (ARIB website) (You will leave the DiBEG website).
| Item | Mode (2k) | Mode (4k) | Mode (8k) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of OFDM segment | 13 | ||
| Useful bandwidth | 5.575 MHz | 5.573 MHz | 5.572 MHz |
| Carrier spacing | 3.968 kHz | 1.984 kHz | 0.992 kHz |
| Number of total carriers | 1405 | 2809 | 5617 |
| Modulation | QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, DQPSK | ||
| Number of symbols / frame | 204 | ||
| Active symbol duration | 252 us | 504 us | 1008 us |
| Guard interval duration | 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32 of active symbol duration | ||
| Inner code | Convolutional code (1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8) | ||
| Outer code | RS(204,188) | ||
| Time interleave | 0 – 0.5 second | ||
| Useful bit rate | 3.651 – 23.234 Mbps | ||
